The most widely used and highly effective synthetic antioxidants are butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), gallates, and tertiary butyl hydroquinone (TBHQ).
BHA is used as an antioxidant for oils and fats either alone or with a gallate and a synergist, such as citric or phosphoric acid.
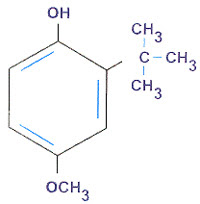 |
| Butylated hydroxyanisole |
Butylated hydroxyanisole is prepared by alkylating p-methoxyphenol with isobutylene or tert-butyl alcohol in the presence of phosphoric acid as a catalyst.
It occurs as a white or slightly yellow, waxy solid having a faint characteristic odor. It is insoluble in water but is freely soluble in alcohol and in propylene glycol. It melts between 49° and 63°.
BHA is used in a wide variety of products, including beverages ice cream, candy, baked foods, gelatin, soup bases, potatoes, glazed fruits, potato flakes, dry breakfast cereals, dry yeasts, dry mixes for desserts and beverages, shortening, smoked dry sausages and emulsions as stabilizers for shortenings.
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA)




